반응형
본 내용은 인프런의 이도원 님의 강의 "Spring Cloud로 개발하는 마이크로서비스 애플리케이션(MSA)" 내용을 바탕으로 정리한 내용입니다.
의존성 추가
pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.modelmapper</groupId>
<artifactId>modelmapper</artifactId>
<version>2.3.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jakarta.validation</groupId>
<artifactId>jakarta.validation-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0.2</version>
</dependency>- JPA와 관련 라이브러리와 ModelMapper를 추가한다.
JPA 관련 파일 추가 의존성 추가
UserEntity 클래스
package com.example.UserService.jpa;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* DB에 저장할 User 데이터
*/
@Data
@Entity
@Table(name="users")
public class UserEntity {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false, length = 50, unique = true)
private String email;
@Column(nullable = false, length = 50)
private String name;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private String userID;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private String encryptedPwd;
}- 데이터베이스에 저장할 사용자 정보를 정의한다.
UserRepository 인터페이스
package com.example.UserService.jpa;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
public interface UserRepository extends CrudRepository<UserEntity, Long> {
}- CrudRepository를 상속받아 데이터베이스와 연결한다.
Dto 추가
UserDto 클래스
package com.example.UserService.dto;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 데이터 이동시 사용
*/
@Data
public class UserDto {
private String email;
private String pwd;
private String name;
private String userId;
private Date createAt;
// 암호화된 패스워드
private String encryptedPwd;
}- 데이터 이동 시 사용할 객체를 정의한다.
Service 추가
UserService 인터페이스
package com.example.UserService.service;
import com.example.UserService.dto.UserDto;
public interface UserService {
UserDto createUser(UserDto userDto);
}- 비즈니스 로직의 기본 구조를 정의한다.
UserServiceImpl 클래스
package com.example.UserService.service;
import com.example.UserService.dto.UserDto;
import com.example.UserService.jpa.UserEntity;
import com.example.UserService.jpa.UserRepository;
import org.modelmapper.ModelMapper;
import org.modelmapper.convention.MatchingStrategies;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.UUID;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Override
public UserDto createUser(UserDto userDto) {
// 랜덤으로 ID 생성
userDto.setUserId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
ModelMapper mapper = new ModelMapper();
// 값들이 정확히 같을 때만 엔티티 클래스로 변환하도록 설정
mapper.getConfiguration().setMatchingStrategy(MatchingStrategies.STRICT);
UserEntity userEntity = mapper.map(userDto, UserEntity.class);
userEntity.setEncryptedPwd("EncryptedPwd");
userRepository.save(userEntity);
UserDto returnUserDto = mapper.map(userEntity, UserDto.class);
return returnUserDto;
}
}- 사용자 생성 로직을 구현한다.
VO 추가
RequestUser
package com.example.UserService.vo;
import lombok.Data;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
import javax.validation.constraints.Size;
/**
* 화면에서 받아오는 정보
*/
@Data
public class RequestUser {
@NotNull(message="Email cannot be null") // Null 입력시 메시지 표시
@Size(min=2, message = "Email not be less than two characters") // 두글자 이상 입력
private String email;
@NotNull(message="Email cannot be null")
@Size(min=2, message = "Email not be less than two characters")
private String name;
@NotNull(message="Email cannot be null")
@Size(min=8, message = "Email not be less than two characters")
private String pwd;
}- 클라이언트로부터 요청받을 데이터를 정의한다.
ResponseUser
package com.example.UserService.vo;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* 반환시 사용할 vo
*/@Data
public class ResponseUser {
private String email;
private String name;
private String userId;
}- 클라이언트로 반환할 데이터를 정의한다.
Conroller 수정
UserController 클래스
package com.example.UserService.controller;
import com.example.UserService.dto.UserDto;
import com.example.UserService.service.UserService;
import com.example.UserService.vo.RequestUser;
import com.example.UserService.vo.ResponseUser;
import org.modelmapper.ModelMapper;
import org.modelmapper.convention.MatchingStrategies;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/")
public class UserController {
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
public UserController(UserService userService){
this.userService = userService;
}
@PostMapping("/users")
public ResponseEntity<ResponseUser> createUser(@RequestBody RequestUser user){
ModelMapper mapper = new ModelMapper();
mapper.getConfiguration().setMatchingStrategy(MatchingStrategies.STRICT);
UserDto userDto = mapper.map(user, UserDto.class);
userDto = userService.createUser(userDto);
ResponseUser responseUser = mapper.map(userDto, ResponseUser.class);
// 정상처리 시 201번 코드를 반환해야 한다.
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).body(responseUser);
}
}- 사용자 정보를 View 받아오고 비즈니스 로직을 호출한다.
회원가입 결과 테스트(postman)
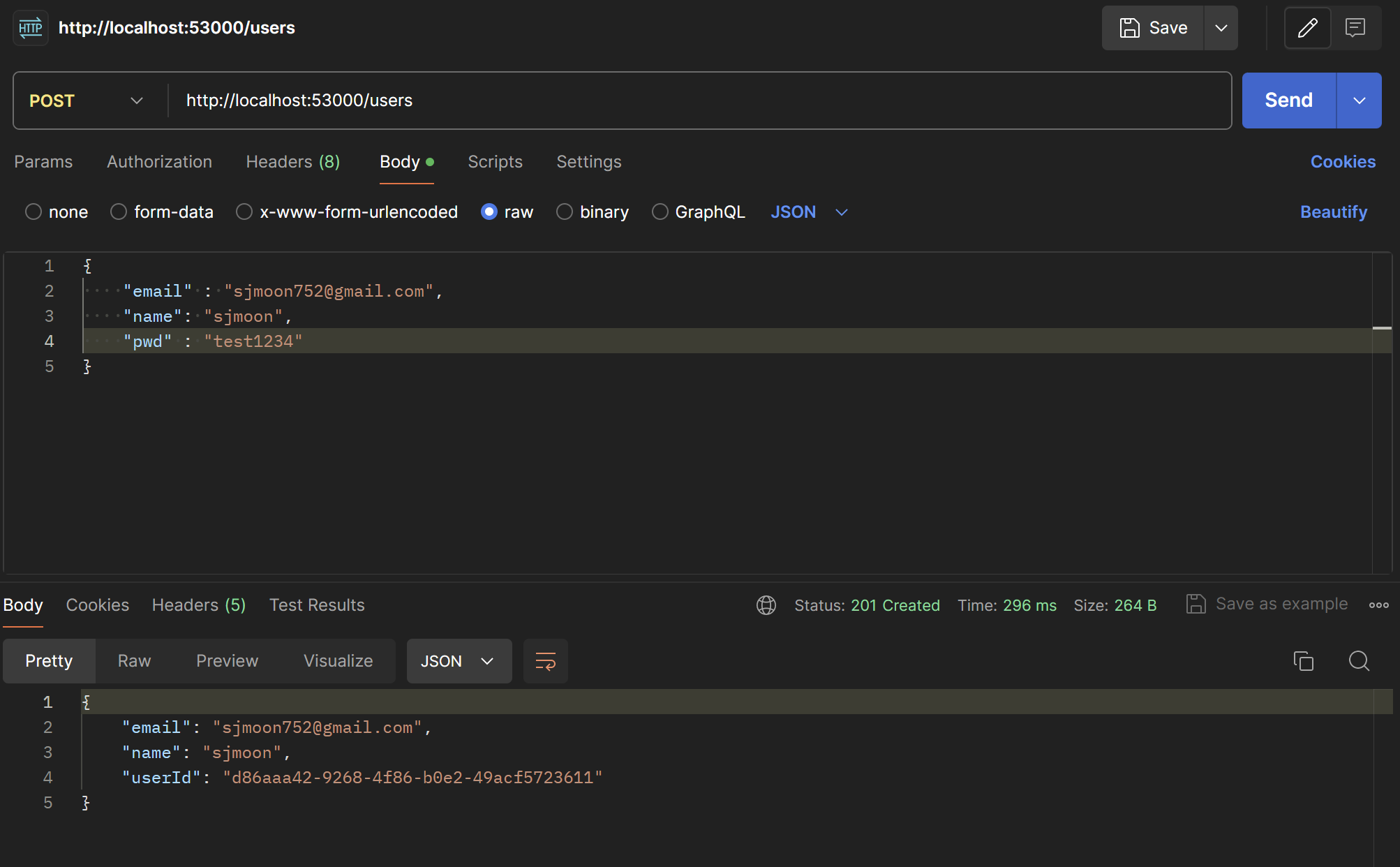
- Body > raw > JSON 형태로 데이터를 입력하고 http://localhost:포트번호/users 로 POST 요청을 보낸다.
- Status가
201 Created로 나오면 성공한 것이다
반응형
'Cloud > MSA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [MSA] MicroService 구현(사용자 서버 기능 추가) (0) | 2024.11.26 |
|---|---|
| [MSA] MicroService 구현(Spring Security) (0) | 2024.11.26 |
| [MSA] MicroService 구현(사용자 서비스) (0) | 2024.06.29 |
| [MSA] Gateway Filter (0) | 2024.06.29 |
| [MSA] Spring Cloud Gateway (0) | 2024.06.29 |